Comprehensive Wound Infection Treatment for Safe Recovery
Wound infections can turn everyday injuries into serious health concerns, leading to complications if not addressed properly. Understanding how these infections develop and manifest is crucial for effective treatment and recovery.
Wound infections can range from minor irritations to chronic conditions, with various risk factors influencing their severity. Familiarizing oneself with the signs, symptoms, and types of infections is the first step to taking control and mitigating risks.
In this article, we will explore wound infections in depth—from their diagnosis and treatment options to the importance of hygiene and prevention strategies. By equipping ourselves with this knowledge, we can better protect ourselves and take proactive steps toward healing.
Understanding Wound Infections
Wound infections occur when germs enter the skin's damaged surface. They can impede the wound healing process, leading to complications. Common sources of infection include bacterial infections and fungal infections.
Types of Infections:
Bacterial Infections: Often caused by Staphylococcus or Streptococcus bacteria. They usually need antibiotic treatment.
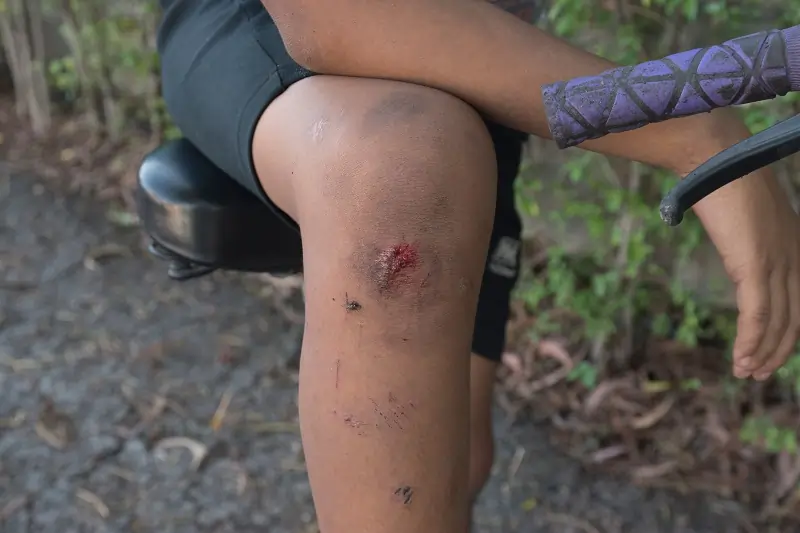
- Fungal Infections: Less common but can arise in moist environments.
Treatment Methods:
- Minor Wound Infections: Clean the wound, apply antiseptic, and bandage it.
- Antibiotic Treatment: Required for serious infections to fight bacteria.
- Surgical Wounds: May need special care to avoid surgical site infection.
- Secondary Intention Healing: When a wound is left open to heal naturally, used for infected wounds.
Signs of Infection:
- Redness
- Swelling
- Pain
- Pus or drainage
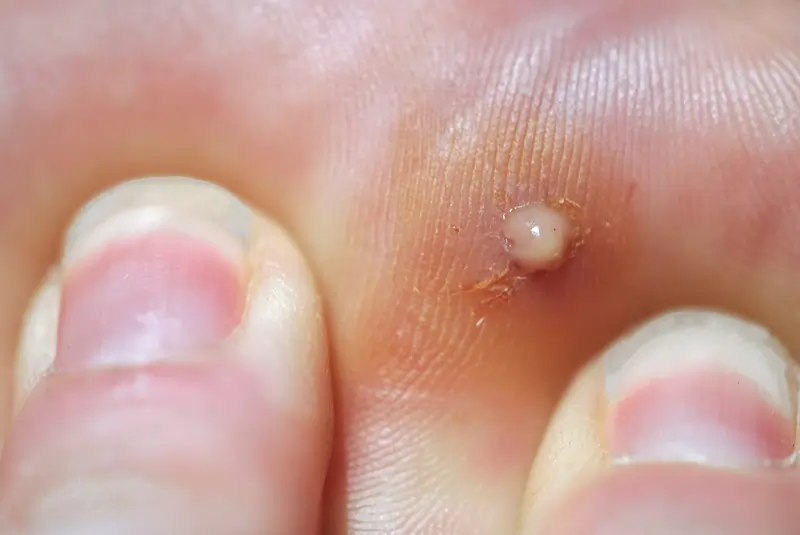
Understanding these infections and their treatments is vital for proper recovery. If signs of infection appear, consult a healthcare provider immediately. Always keep wounds clean and dry to prevent infection.
Signs and Symptoms of Wound Infections
Wound infections can slow the healing process. Recognizing the signs and symptoms is crucial for timely treatment.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Wound Infections:
-
- Redness and Swelling: Infected wounds are often red and swollen. The area may feel warm to the touch.
- Pain and Tenderness: Increased pain or tenderness around the wound can signal an infection.
- Pus or Discharge: A thick, yellow or green discharge from the wound is a clear sign of infection.
- Foul Odor: An unpleasant smell coming from the wound indicates bacterial or fungal infections.
- Delayed Healing: If a wound is not healing within the expected timeframe, it may be infected.
- Fever: A fever might accompany wound infections as your body fights bacteria.
| Sign or Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Redness & Swelling | Red, warm, and swollen skin around the wound |
| Pain & Tenderness | Increased discomfort in the affected area |
| Pus or Discharge | Thick yellow or green fluid from the wound |
| Foul Odor | Bad smell emanating from the wound |
| Delayed Healing | Slower than expected wound recovery |
| Fever | Elevated body temperature |
If you notice any of these symptoms, seek medical attention. Early intervention with proper antibiotic treatment can prevent complications.
Risk Factors for Wound Infections
Wound infections can complicate recovery. Understanding risk factors helps in taking preventive steps. Here are some key risk factors for developing wound infections:
- Type of Wound: Surgical wounds and traumatic injuries are prone to infections. Open wounds have higher risks compared to closed ones.
- Immune System Status: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes or HIV, are more susceptible to bacterial infections.
- Poor Blood Circulation: Conditions like peripheral artery disease can hinder the wound healing process, increasing the infection risk.
- Hygiene: Poor hygiene and improper wound care can introduce harmful bacteria or fungi, leading to infections.
- Nutritional Deficiency: Lack of adequate nutrition can slow down healing and make wounds more prone to infection.
- Smoking and Alcohol Use: Both can impair blood flow and immune response, increasing infection chances.
Risk Factors Table
| Risk Factor | Impact on Wound Infection |
|---|---|
| Type of Wound | Open wounds at higher risk |
| Immune System Status | Weakened immunity increases risk |
| Blood Circulation | Poor circulation hinders healing |
| Hygiene | Poor hygiene introduces bacteria |
| Nutritional Deficiency | Slows healing, ups infection risk |
| Smoking/Alcohol | Impairs blood flow/immune response |
Addressing these factors can greatly reduce the likelihood of wound infections.
Types of Wound Infections
Wound infections can vary in severity and cause. Knowing the type of infection is crucial for treatment.
Minor Wound Infections
Minor wound infections are usually localized and cause redness, swelling, and mild pain. These infections occur often on superficial cuts, scrapes, or abrasions. They are typically caused by bacteria entering through broken skin. Proper wound care is essential to prevent them from becoming serious.
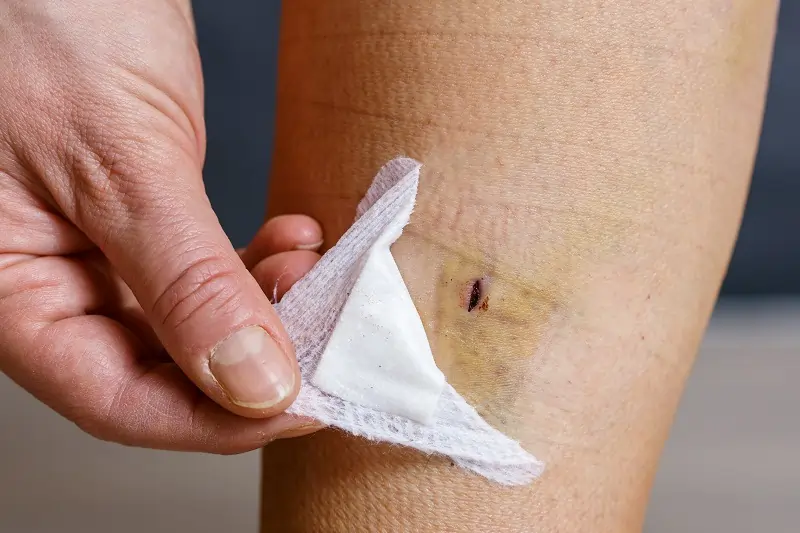
Symptoms of Minor Wound Infections:
- Redness around the wound
- Mild swelling
- Slight pain or tenderness
- Clear or slightly cloudy discharge
Treatment often involves cleaning the wound and applying an antibiotic ointment. Keeping the wound clean and dry can promote faster healing.
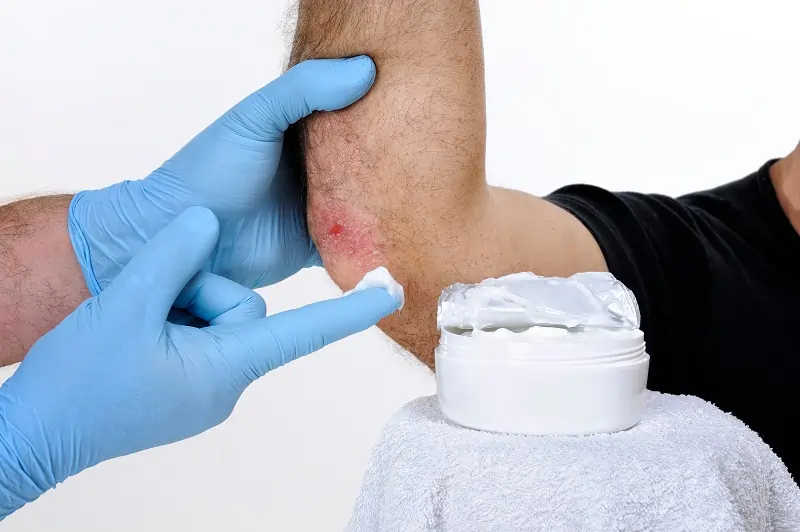
Chronic Wound Infections
Chronic wound infections are more serious and can persist for weeks or even months. They may arise in wounds that fail to heal properly, such as ulcers or bedsores. Factors like poor circulation and immune system issues contribute to their development.
Symptoms of Chronic Wound Infections:
- Persistent redness and swelling
- Pain that does not subside
- Pus or unusual discharge
- Foul odor emanating from the wound
Treatment for chronic infections may require oral antibiotics or specialized wound care. Addressing underlying health conditions is crucial for healing. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider often helps prevent complications.
Diagnosis of Wound Infections
Wound infections can impede the healing process and lead to complications. Early diagnosis is key to effective treatment. Addressing an infected wound soon can prevent further problems.
Clinical Assessment
Clinical assessment is the first step in diagnosing wound infections. Look for signs such as redness, swelling, and warmth around the wound. Pain and ooze from the wound can also suggest infection. In some cases, the wound may have a foul smell. These symptoms can indicate a bacterial or fungal infection.
Doctors may also assess the type of wound. Minor wound infections have different signs than surgical site infections. The healing process may slow down or stop if the wound is infected. Monitoring these signs helps in understanding whether the wound heals by primary or secondary intention.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests confirm the presence and type of infection. These tests help identify if bacteria or fungi are causing the infection. A common test is a wound culture, which checks for bacterial infections by growing bacteria from the wound.
Another useful test is a blood test to see if your body is fighting an infection. The results guide doctors on the best course of antibiotic treatment. Sometimes, imaging tests help if deeper tissue infection is suspected.
Here's a simple table to summarize:
| Test Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Wound Culture | Identifies bacteria causing the infection |
| Blood Test | Confirms body-wide infection signs |
| Imaging Tests | Checks for deep tissue infections |
These methods help in deciding the best treatment plan to ensure proper healing of infected wounds.
Treatment Modalities
Treating wound infections involves various methods tailored to the type and severity of the infection. It is essential to choose the right approach to promote healing and prevent complications.
Natural Remedies
For minor wound infections, natural remedies can be helpful. Here are some options:
- Honey: Known for its antibacterial properties, honey can help reduce the risk of infection.
- Aloe Vera: This plant may soothe the skin and speed up healing.
- Tea Tree Oil: Its antifungal and antibacterial properties make it useful for treating minor cuts and wounds.
Always clean the wound before applying any natural remedy to ensure effectiveness.
Antimicrobial Agents
Antimicrobial agents are crucial in the wound healing process, especially for bacterial and fungal infections. Here's a brief overview:
- Antibiotic treatment: Applied topically or taken orally to combat bacterial infections.
- Antifungal creams: Used for fungal infections that may develop in warm, moist areas.
Doctors may prescribe antibiotics for surgical site infections or infected wounds that do not respond to over-the-counter options.
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgical interventions are necessary. These are typically used for more severe or chronic infections:
- Debridement: A procedure to remove dead or infected tissue from the wound to promote healing.
- Secondary intention: Allowing the wound to heal naturally without closing it surgically.
Surgical wounds, particularly those that become infected, may require specialized treatment to prevent further complications.
By understanding these treatment modalities, you can be better prepared to manage wound infections effectively.
Importance of Wound Hygiene
Proper wound hygiene is essential for a smooth healing process. Clean wounds are less likely to become infected, allowing quicker recovery. Infections can occur due to bacteria, fungi, and other microbes. For successful wound healing, it's important to follow these steps:
- Cleanliness: Wash your hands before touching a wound. Use mild soap and water to clean the area gently.
- Antiseptic Use: Apply a suitable antiseptic to kill germs without harming the tissue.
- Protect the Wound: Cover it with a sterile bandage to keep dirt and bacteria out and to retain moisture, aiding in faster healing.
- Monitoring: Check for signs of infection such as redness, swelling, or pus. Early detection allows prompt treatment with antibiotics if needed.
- Changing Dressings: Regularly change the dressing to keep the wound clean and dry.
The following table summarizes prevention for different infections:
| Infection Type | Prevention Tips |
|---|---|
| Bacterial | Use antibiotics if needed |
| Fungal | Keep the area dry |
| Surgical Wounds | Follow post-op care |
Practicing good wound hygiene minimizes the risk of complications like surgical site infections and supports healing by secondary intention. Keep it clean, and let your body do the rest!
Prevention Strategies
Wound infections can delay healing, so preventing them is crucial. Key strategies include keeping wounds clean and using appropriate protective measures. Recognizing the type of infection risk, such as bacterial or fungal, is also important. By adopting proper care habits, you decrease the chance of infection and promote faster recovery.
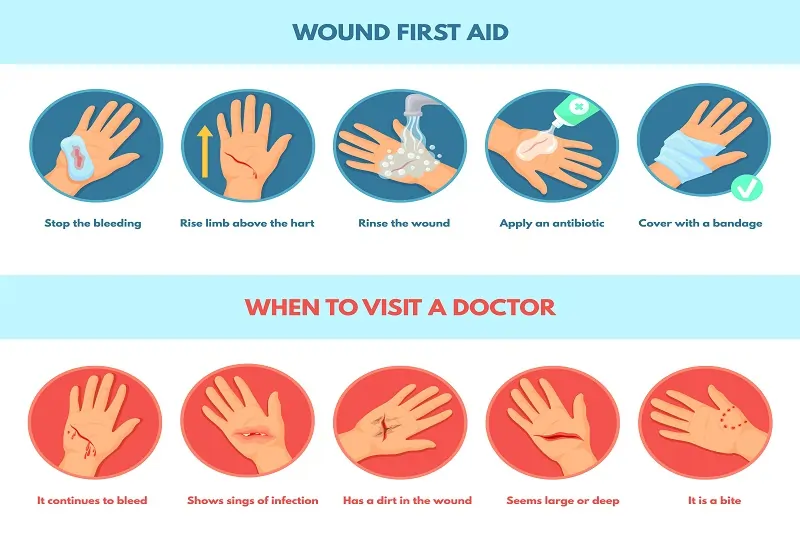
Proper Wound Care
Taking care of a wound properly can prevent infections and speed up recovery. Start by washing your hands before touching the wound to avoid introducing germs. Clean the wound gently with mild soap and water. Use an antiseptic to kill any remaining germs without damaging skin tissue. Protect the wound with a sterile bandage to prevent dirt and bacteria from entering, which also helps it stay moist for better healing. Always check for signs of infection like redness or swelling. If you notice any, consider antibiotic treatment right away.

Lifestyle Changes
Certain lifestyle changes can lower your risk of wound infections. Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports the body’s natural healing process. Regular exercise can boost your immune system, making it more effective at fighting infections. Staying hydrated and getting enough sleep are also important, as they contribute to overall health and wound recovery. By maintaining good hygiene and making these positive lifestyle adjustments, you can help prevent complications like minor wound infections and surgical site infections.
Here’s a quick guide for easy reference:
| Lifestyle Change | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Balanced Diet | Provides essential nutrients for healing |
| Regular Exercise | Strengthens immune system |
| Hydration | Aids cell repair and regeneration |
| Proper Sleep | Supports immune function |
Implement these changes, and keep your wound care routine consistent for the best results.
When to Seek Medical Attention
When to Seek Medical Attention for Wound Infections
Wound infections can vary in severity. Knowing when to seek medical help is crucial to prevent complications. Here are some signs to watch out for:
- Persistent Redness and Swelling: If redness and swelling increase instead of improving, this can be a sign of an infection.
- Pain: Persistent or worsening pain around the wound site may need medical attention.
- Drainage and Odor: Yellow or green pus and a foul smell indicate a possible bacterial infection.
- Warmth around the Wound: An unusually warm area around the wound may suggest inflammation.
- Fever: A fever could mean the infection is spreading.
For those with surgical wounds or those healing by secondary intention, it's crucial to monitor these signs closely. Delayed wound healing can occur without medical care.
Wound Type and Symptoms
| Wound Type | Symptoms Requiring Attention |
|---|---|
| Minor Wound | Increased redness, pus, fever |
| Surgical Infection | Pain, prolonged swelling, drainage |
| Infected Wounds | Intense warmth, spreading redness |
Remember, timely medical treatment and proper care, possibly including antibiotic treatment, can help ensure a smooth wound healing process.